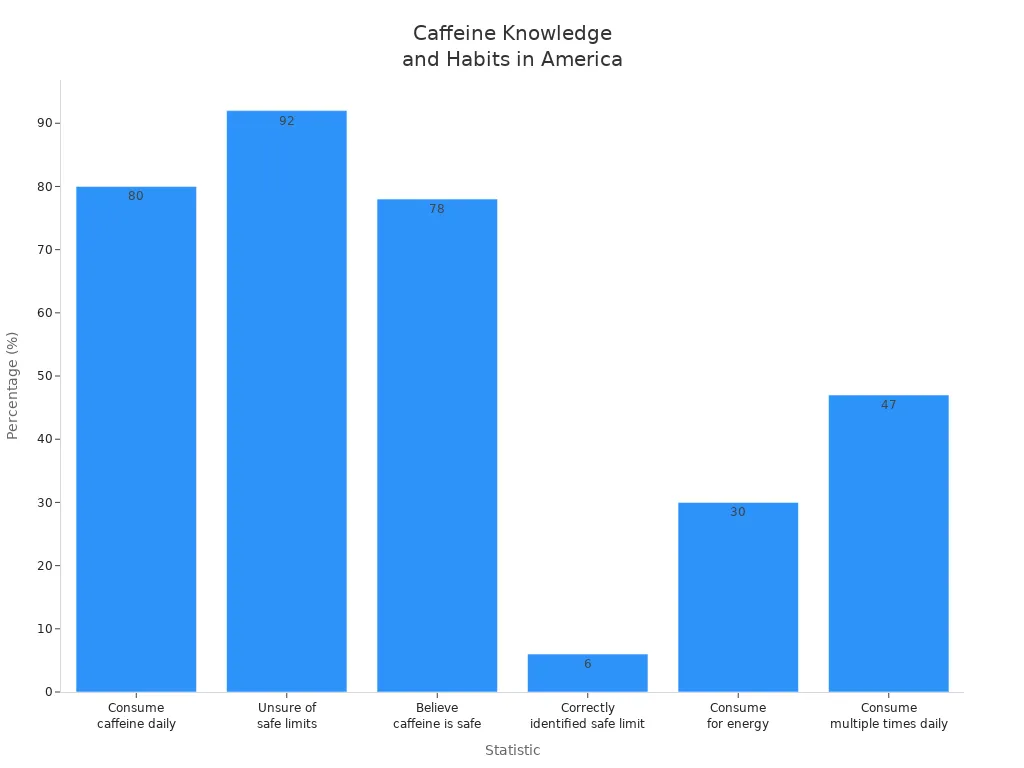
You often wonder how much caffeine in a cup of coffee you drink each morning. An 8 oz cup of brewed coffee usually gives you 80–100 mg of caffeine. Coffee stands out for its high caffeine content compared to tea or energy drinks. Knowing these numbers helps you make smart choices every day.
Key Takeaways
An 8 oz cup of brewed coffee typically contains 80–100 mg of caffeine. Knowing this helps you manage your daily intake.
Different coffee types have varying caffeine levels. Brewed coffee has the most, while decaf has the least.
The U.S. FDA recommends a daily caffeine limit of 400 mg for most adults. Staying within this limit can help avoid negative side effects.
How Much Caffeine in a Cup of Coffee

Average Amount
When you ask how much caffeine in a cup of coffee, you find that the answer can change depending on many things. On average, an 8-ounce cup of brewed coffee contains about 95 milligrams of caffeine. Most cups fall within a range of 70 to 140 milligrams. Some laboratory tests show that the caffeine content can be as low as 12.8 milligrams or as high as 309.4 milligrams in a single serving. This wide range happens because coffee comes from different beans, brewing methods, and serving sizes.
If you drink coffee every day, knowing how much caffeine in a cup of coffee helps you manage your energy and avoid having too much.
By Coffee Type
Not all coffee drinks have the same amount of caffeine. The type of coffee you choose makes a big difference. Brewed coffee, which most people drink at home or in cafes, usually has the highest caffeine per cup. Espresso is much stronger per ounce, but you usually drink it in smaller amounts. Instant coffee has less caffeine than brewed coffee, but it can still give you a boost. Decaf coffee is not completely caffeine-free, but it has much less caffeine than regular coffee.
Here are some typical caffeine amounts for each type:
Brewed coffee: About 95 mg per 8 oz cup
Espresso: About 63 mg per 1 oz shot (more concentrated, but smaller serving)
Instant coffee: Usually 60–80 mg per 8 oz cup
Decaf coffee: Only 2–5 mg per 8 oz cup
Some specialty coffees, like Death Wish Coffee or Black Insomnia, can have extremely high caffeine levels. These drinks may contain up to 1,500 mg of caffeine in a 12-ounce serving. Most people do not drink these types every day, but it shows that how much caffeine in a cup of coffee can sometimes be much higher than average.
Quick Comparison Table
You can use the table below to compare the caffeine content in different types of coffee. This helps you see at a glance how much caffeine in a cup of coffee you might get, depending on what you choose.
Type of Coffee |
Caffeine Content (mg) |
Serving Size (oz) |
|---|---|---|
Brewed Coffee |
95 |
8 |
Espresso |
63 |
1 |
Instant Coffee |
60–80 |
8 |
Decaf Coffee |
2–5 |
8 |
Specialty Coffee |
500+ (rare) |
varies |
☕️ Some commercial coffee servings, especially large "takeaway" drinks, can exceed 500 mg of caffeine. Always check the size and type before you drink.
When you think about how much caffeine in a cup of coffee, remember that the answer depends on the type, the serving size, and even the brand. Most cups will not reach the extreme levels found in specialty coffees, but it is possible to go over the recommended daily limit if you drink several strong coffees in one day.
Factors Affecting Caffeine
Bean Type
The type of coffee bean you choose has a big impact on how much caffeine ends up in your cup. Arabica and Robusta are the two most common beans. Robusta beans have about twice as much caffeine as Arabica beans. If you want a stronger kick, Robusta is the way to go. Here is a quick comparison:
Coffee Type |
Caffeine in 12 oz (mg) |
|
|---|---|---|
Arabica |
1.5% |
98 |
Robusta |
2.7% |
190 |
A typical 8 oz cup of Robusta coffee contains 140–200 mg of caffeine, while Arabica gives you 70–130 mg. This difference explains why some cups feel much stronger than others.
Roast Level
You might think dark roast coffee has more caffeine, but that is not true. Both light and dark roast beans have similar caffeine levels per bean. The roasting process changes the flavor and color, but it does not change caffeine much. When you measure by weight, the difference is very small. Some studies show that dark roast beans lose a little caffeine during roasting, but the change is not enough to notice in your daily cup.
Tip: If you want to control how much caffeine in a cup of coffee, focus more on the bean type than the roast level.
Brewing Method
The way you brew your coffee also affects caffeine content. Some methods pull out more caffeine from the grounds. For example, cold brew and drip coffee usually have more caffeine than French press. Espresso packs a lot of caffeine in a small shot. Here is a table to help you compare:
Brewing Method |
|
|---|---|
Espresso |
60-65 mg per 1 oz shot |
Cold Brew |
155-240 mg per 12 oz serving |
Drip Coffee |
95-165 mg per 8 oz cup |
French Press |
80-135 mg per 8 oz cup |
Coffee-to-Water Ratio
The amount of coffee grounds you use compared to water changes how strong your drink will be. A higher coffee-to-water ratio means more caffeine per cup. Different brewing methods use different ratios. Here is a chart that shows how ratios can change the strength of your coffee:
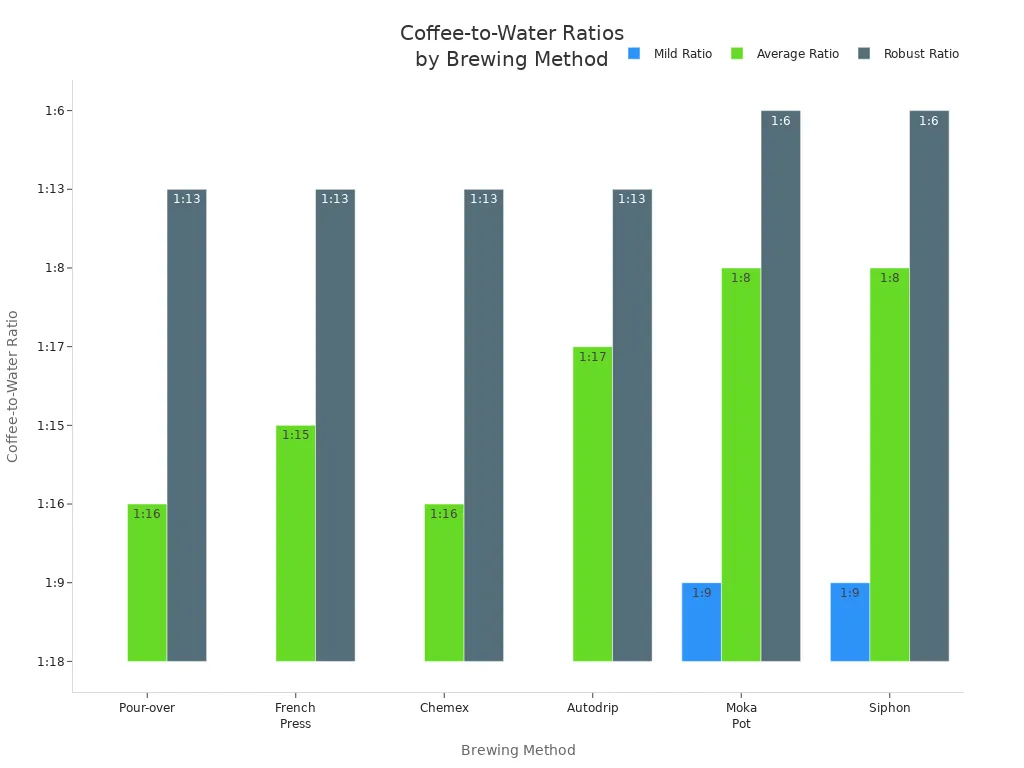
If you want less caffeine, use fewer grounds or more water. If you want a stronger cup, use more coffee grounds.
Daily Intake & Health
Safe Limits
You need to know how much caffeine is safe each day. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) says most adults can safely have up to 400 milligrams of caffeine per day. This equals about four cups of regular coffee. If you are pregnant or a teenager, your safe limit is lower. Check the table below for guidance:
Group |
Safe Limit (mg/day) |
|---|---|
Healthy Adults |
400 |
Pregnant Individuals |
< 200–300 |
Adolescents (12–18 years) |
< 100 |
Children (<12 years) |
< 2.5 mg/kg |
You might feel fine with less caffeine, or you might notice side effects if you have too much. Your body size, age, and health all play a role.
Too much caffeine can cause problems like anxiety, rapid heart rate, insomnia, and high blood pressure. Some people also feel irritable or get headaches if they stop caffeine suddenly.
Health Tips
You can enjoy coffee and still stay healthy by following a few simple tips:
Track your caffeine intake. Write down what you drink to spot patterns.
Stop drinking caffeine by mid-afternoon to help you sleep better.
Drink water along with coffee to stay hydrated.
Try half-caf or decaf coffee, herbal teas, or smoothies for a lighter boost.
Mix regular coffee with decaf to slowly cut back if you want less caffeine.
Caffeine can help you feel alert and improve your mood. If you keep your intake within safe limits, you lower your risk of sleep problems and heart issues. Always listen to your body and adjust your habits if you notice any side effects.
You now know the average caffeine content in coffee, the main factors that affect it, and the safe daily limit of 400 mg. Use this table to remember what matters most:
Factor |
Key Point |
|---|---|
Coffee Bean Type |
Robusta has more caffeine than Arabica |
Roast Level |
Light and medium roasts have more caffeine |
Brewing Method |
Hotter water extracts more caffeine |
Safe Daily Limit |
400 mg for healthy adults |
Stay within healthy limits by tracking your intake, choosing decaf when needed, and avoiding late-day coffee.
FAQ
How does decaf coffee still have caffeine?
Decaf coffee goes through a process that removes most caffeine, but not all. You still get a small amount, usually 2–5 mg per cup.
Can you build a tolerance to caffeine?
You can build a tolerance if you drink coffee every day. Over time, you may need more caffeine to feel the same effects.
Does iced coffee have more caffeine than hot coffee?
Iced coffee uses the same beans as hot coffee. The caffeine amount depends on how you brew it, not the temperature.
Tip: Always check serving size for accurate caffeine content.